A Guide to Creating and Managing a VPC NAT Gateway on Alibaba Cloud

Introduction:
NAT Gateway is a crucial component of the network infrastructure on Alibaba Cloud. It provides a secure and efficient way to connect your virtual private cloud (VPC) to the internet, allowing your resources to access external networks while maintaining control over inbound and outbound traffic.
In this blog post, we will explore the concept of NAT Gateway and its benefits within the Alibaba Cloud ecosystem.
What is NAT Gateway?
NAT Gateway is a managed network address translation (NAT) service offered by Alibaba Cloud. It acts as an intermediary between your private network (VPC) and the public internet, enabling instances within your VPC to communicate with the outside world.
It translates private IP addresses to public IP addresses, allowing multiple instances to share a limited number of public IP addresses.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Outbound Connectivity: NAT Gateway enables instances in your VPC to access the internet for software updates, patching, and other external resources. It allows outbound connections initiated by instances while protecting your internal resources by hiding their private IP addresses.
- Inbound Access Control: NAT Gateway provides granular control over inbound traffic. You can define access rules to allow or deny specific inbound connections, enhancing the security of your VPC and preventing unauthorized access.
- Scalability and High Availability: Alibaba Cloud's NAT Gateway service is designed to handle high traffic loads and scale as your business grows. It automatically adjusts resources based on demand, ensuring a reliable and consistent network performance.
- Service Integration: NAT Gateway seamlessly integrates with other Alibaba Cloud services, such as Elastic Compute Service (ECS), Server Load Balancer (SLB), and Virtual Private Network (VPN). This integration simplifies network configuration and management, making it easier to deploy and manage your resources.
- Cost-Effective: By using NAT Gateway, you can reduce the number of public IP addresses required for your VPC, as multiple instances can share a single IP. This optimization helps to minimize costs while maintaining connectivity.
Prerequisites:
- An Alibaba Cloud account
- A VPC already set up in your Alibaba Cloud account
Lab Steps:
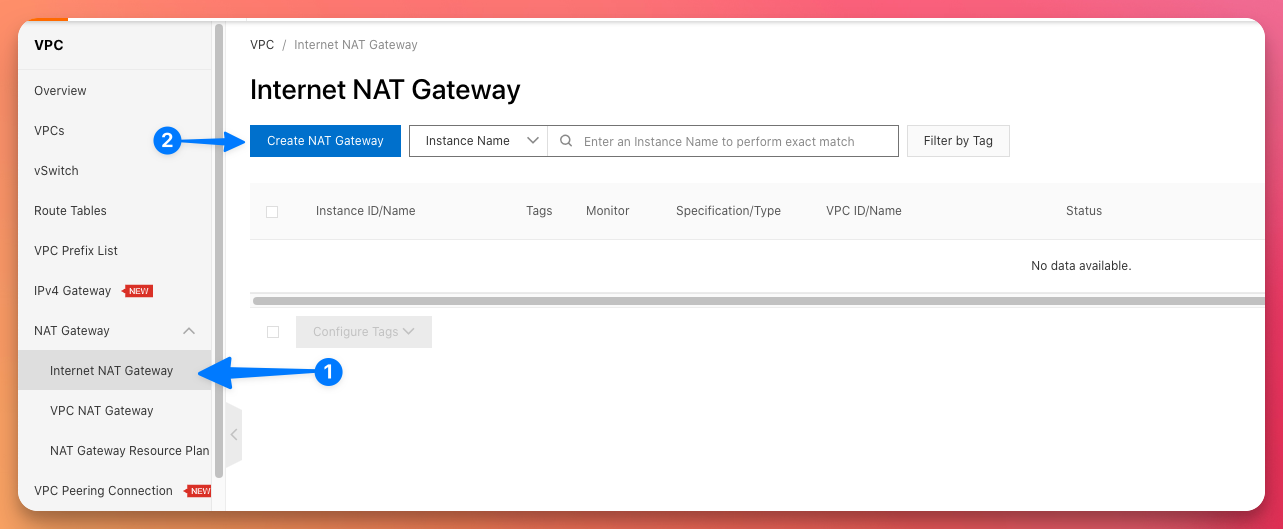
Step 1: Create an Internet NAT Gateway
- Log in to the Alibaba Cloud Console.
- Navigate to the VPC section and select "NAT Gateway" from the left-hand menu.
- Click on the "Create NAT Gateway" button.
- Configure the NAT Gateway by specifying the VPC, region, and bandwidth requirements.
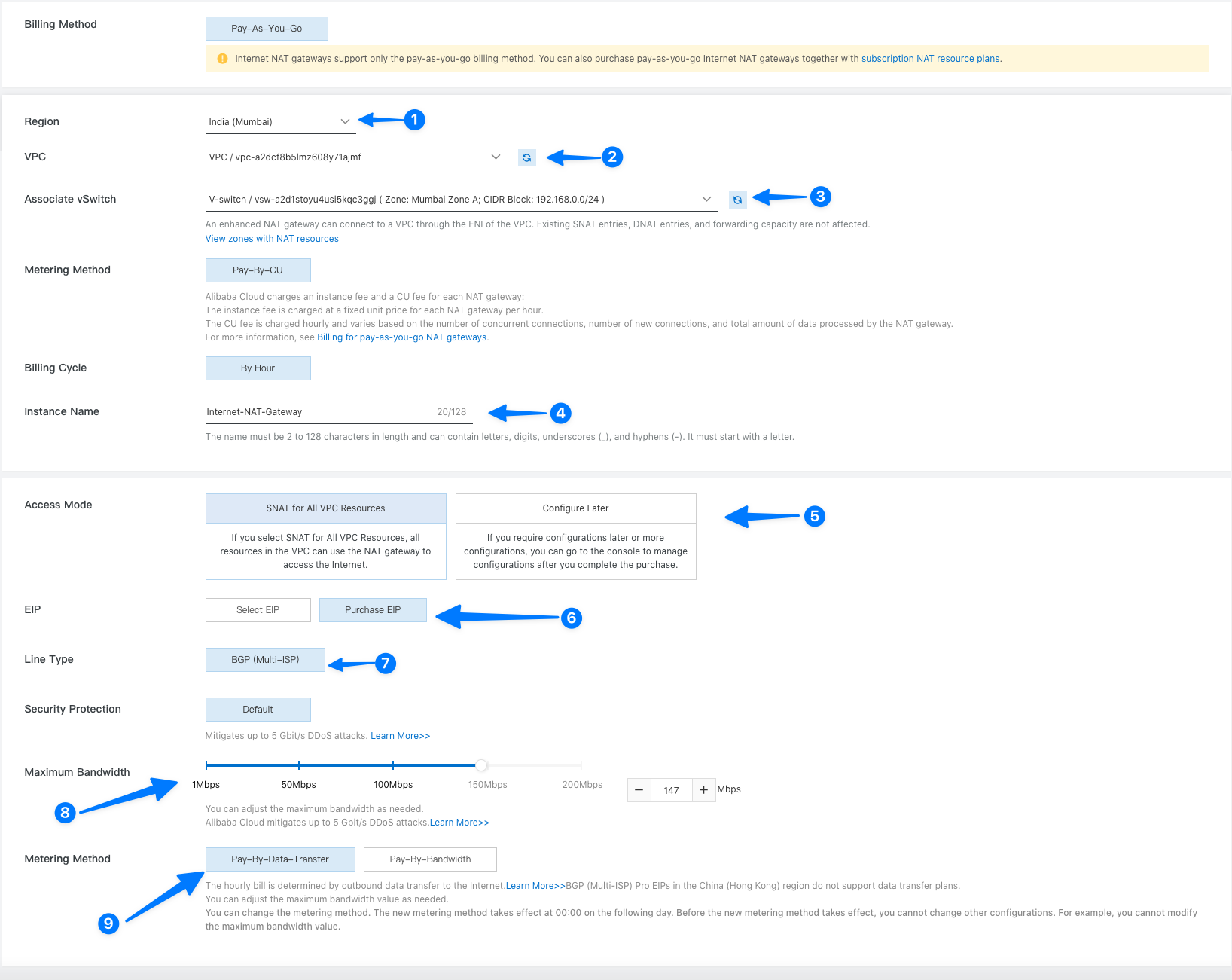
- Assign an Elastic IP address to the NAT Gateway to enable internet access.
- Review the settings and click on "Create" to create the NAT Gateway.
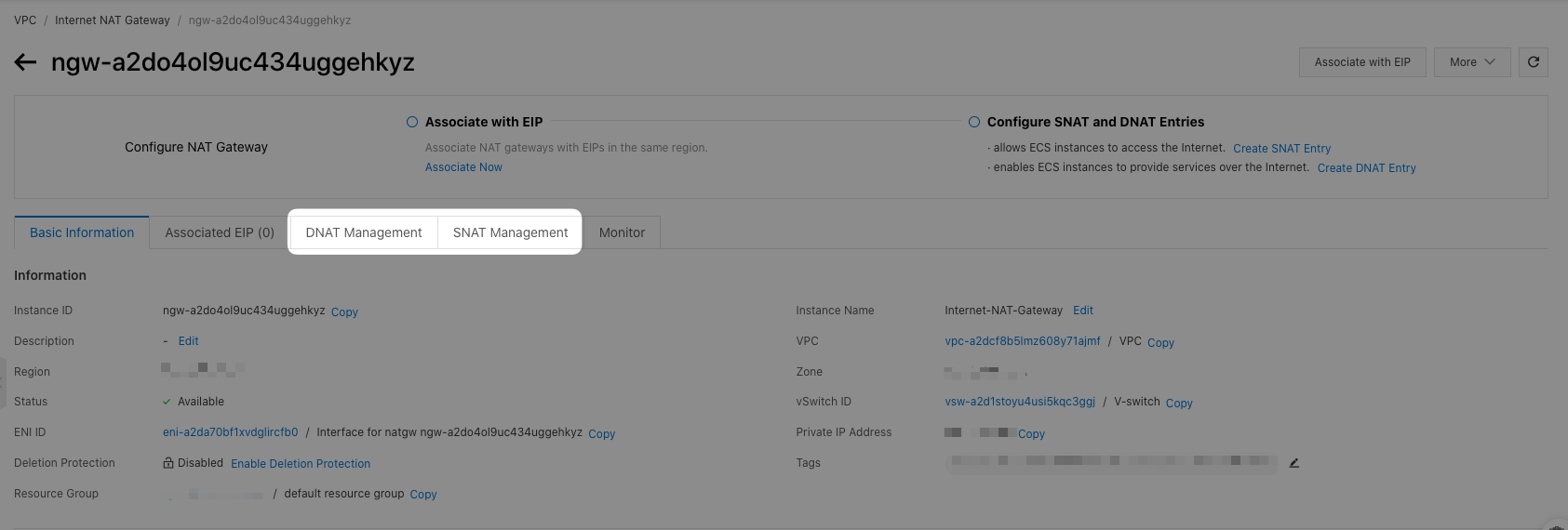
Step 2: Configure SNAT and DNAT Rules
- After the NAT Gateway is created, go to the "NAT Gateway" page in the console.
- Select the desired NAT Gateway instance.
- Configure the Source Network Address Translation (SNAT) rule to allow instances within your VPC to access the internet.
- Configure the Destination Network Address Translation (DNAT) rule to forward inbound traffic to specific instances within your VPC.
- Save the changes.
Step 3: Test Internet Connectivity
- Launch an ECS instance within the same VPC as the NAT Gateway.
- Verify that the ECS instance is using the NAT Gateway as its default gateway.
- Attempt to access the internet from the ECS instance by pinging a public IP address.
- Confirm that the ECS instance can successfully connect to the internet.
Step 4: Manage and Monitor NAT Gateways
Conclusion:
Creating and managing a VPC NAT Gateway on Alibaba Cloud is a fundamental aspect of building a secure and efficient network infrastructure.
By following the steps outlined in this blog post, you can successfully create a VPC NAT Gateway, configure SNAT and DNAT rules, and enable outbound internet connectivity for your VPC resources.
The VPC NAT Gateway provides a reliable and scalable solution, ensuring secure communication between your VPC and external networks while maintaining control over outbound traffic.