Server Migration to Alibaba Cloud

Migrating to the cloud from a traditional data center offers a range of benefits that can significantly impact an organization's efficiency, scalability, and overall performance. Here are key bullet points outlining the advantages of planning a migration to the cloud:
1. Cost Efficiency:
- Pay-as-You-Go Model:
- Pay only for the resources consumed, reducing upfront infrastructure costs.
- Economies of Scale:
- Leverage cloud providers' infrastructure to benefit from cost savings due to large-scale operations.
2. Scalability and Flexibility:
- On-Demand Resources:
- Scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance.
- Flexibility to Experiment:
- Easily test new applications or features without major infrastructure investments.
3. Global Reach:
- Geographical Expansion:
- Deploy applications and services globally with ease, reaching a broader audience.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs):
- Leverage CDNs for faster content delivery and improved user experience.
4. Agility and Speed:
- Rapid Deployment:
- Quickly deploy applications and updates, reducing time-to-market.
- Automated Processes:
- Implement automation for tasks like provisioning, scaling, and maintenance.
5. Security and Compliance:
- Robust Security Measures:
- Cloud providers invest heavily in security infrastructure, offering advanced protection.
- Compliance Services:
- Utilize built-in compliance tools and certifications to meet regulatory requirements.
6. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity:
- Data Redundancy:
- Benefit from multiple data centers and geographic redundancy for enhanced data durability.
- Automated Backups:
- Implement automated backup and recovery processes for improved resilience.
7. Innovation and Access to Latest Technologies:
- Access to Cutting-Edge Tools:
- Take advantage of cloud providers' continuous innovation and integration of the latest technologies.
- Focus on Core Competencies:
- Shift the focus from infrastructure management to innovation and core business activities.
8. Collaboration and Remote Work:
- Collaborative Tools:
- Use cloud-based collaboration tools for seamless communication and teamwork.
- Remote Accessibility:
- Enable employees to access data and applications from anywhere, fostering remote work.
9. Environmental Sustainability:
- Energy Efficiency:
- Cloud providers optimize resource usage, leading to reduced energy consumption.
- Green Initiatives:
- Many cloud providers are committed to sustainability, aligning with environmental goals.
10. Cost Predictability and Management:
- Transparent Billing:
- Receive detailed billing statements, allowing for better cost management.
- Resource Monitoring:
- Utilize monitoring tools to track resource usage and identify cost-saving opportunities.
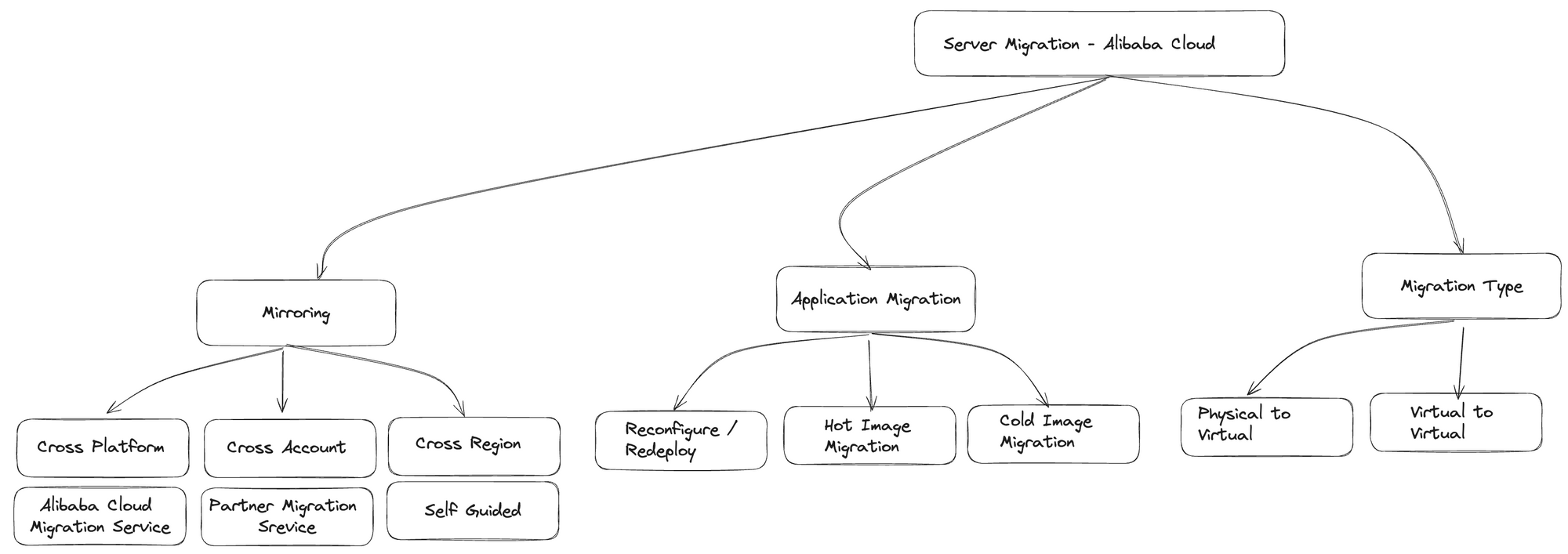
Server Migration Strategy
Migrating servers to Alibaba Cloud can be achieved through various methods, each tailored to specific needs. Here's an overview of the different ways to migrate servers to Alibaba Cloud, with a focus on mirroring:
1. Mirroring:
Cross-Platform Migration using Alibaba Cloud Migration Service
- Leverage Alibaba Cloud Migration Service for seamless migration across different platforms.
- This service supports both Windows and Linux operating systems.
- Provides a fast and efficient migration process.
Third-Party Tools:
- Explore tools like Disk2VHD, Linux DD Command, Xen Convert, Starwind, and Qemu-img.
- Assess compatibility with the operating systems to ensure a smooth migration.
- These tools can be especially useful for heterogeneous environments.
Assessment:
- Conduct a thorough assessment of the existing server environment.
- Ensure compatibility and prepare for any adjustments required for Alibaba Cloud.
2. Cross-Account Migration:
Partner Migration Service:
- Collaborate with Alibaba Cloud partners who offer specialized migration services.
- Leverage their expertise for a smooth and efficient cross-account migration.
GUI or Open API:
- Use Alibaba Cloud's user-friendly graphical user interface (GUI) for simplified migration.
- Alternatively, employ Alibaba Cloud's Open API for programmatic and automated migration.
3. Cross-Region Migration:
Self-Guided Migration:
- Initiate a self-guided migration process to move servers across Alibaba Cloud regions.
- This method provides more control over the migration timeline and configuration.
GUI or Open API:
- Utilize Alibaba Cloud's graphical user interface or Open API for cross-region migration.
- Leverage the flexibility of Alibaba Cloud's tools for a customized migration experience.
Best Practices for Alibaba Cloud Server Migration:
Backup and Disaster Recovery:
- Prioritize data backup before migration to ensure data integrity.
- Implement disaster recovery measures for unforeseen issues during migration.
Network Considerations:
- Optimize network configurations to minimize downtime and ensure smooth data transfer.
- Consider Alibaba Cloud's networking features for enhanced performance.
Security and Compliance:
- Align migration processes with security best practices and compliance standards.
- Leverage Alibaba Cloud's security features to enhance the overall security posture.
Monitoring and Validation:
- Implement monitoring tools to track the migration process in real-time.
- Validate the migrated servers to ensure they operate seamlessly in the Alibaba Cloud environment.
Application Migration Strategies
Migrating applications or servers to a new environment can be approached in different ways, each with its own set of characteristics. Let's explore the three methods you mentioned:
1. Redeployment / Reconfiguration:
Speed:
- Slow compared to other methods.
Effort:
- Requires more effort as applications need to be reconfigured for the new environment.
Complexity:
- The process can be complicated due to differences in infrastructure and configurations.
Human Interaction:
- Involves significant human interactions for adjusting configurations and resolving compatibility issues.
2. Image Migration - Cold:
Process:
- Images are migrated directly to the cloud provider in a cold state (offline).
Speed:
- Fast with a high rate of success.
Human Interaction:
- Requires less human interaction compared to redeployment.
Downtime:
- Involves downtime during the migration process.
3. Image Migration - Hot:
Process:
- Images are migrated directly to the cloud provider in a hot state (online).
Speed:
- Fast with a high rate of success.
Human Interaction:
- Requires less human interaction compared to redeployment.
Downtime:
- Typically does not require downtime, but data synchronization may be needed to ensure consistency.
Considerations for Choosing a Migration Method:
Redeployment / Reconfiguration:
- Suitable for complex applications that require significant adjustments.
- Appropriate when the migration process can be gradual, and downtime is not a critical concern.
Image Migration - Cold:
- Ideal for applications with acceptable downtime during the migration process.
- Recommended for scenarios where a clean, fast migration is more critical than continuous availability.
Image Migration - Hot:
- Suitable for applications that require minimal to no downtime during migration.
- Ideal for environments where continuous operation is a top priority.
Best Practices:
Plan and Test:
- Thoroughly plan the migration strategy, considering the specific requirements of the applications.
- Conduct testing, especially for complex configurations, to identify potential issues beforehand.
Backup and Rollback:
- Implement a robust backup strategy before migration.
- Have a rollback plan in case unexpected issues arise during or after migration.
Communication:
- Clearly communicate the migration plan and any potential downtime to stakeholders.
- Keep users informed about the expected impact on services.
Monitoring:
- Implement monitoring tools to track the migration progress and detect any anomalies.
- Monitor application performance post-migration to ensure optimal operation.
Server Migration Types
Indeed, when it comes to server migration, two common types are Physical to Virtual (P2V) and Virtual to Virtual (V2V) migrations. Let's delve into the characteristics of each:
1. Physical to Virtual (P2V) Migration:
Definition:
- In P2V migration, the goal is to move an entire physical server's operating system, applications, and data to a virtualized environment.
Process:
- The physical server is replicated or imaged, and the resulting image is deployed as a virtual machine (VM) in a virtualized environment.
Use Cases:
- Legacy hardware replacement: When physical servers are aging or becoming obsolete, migrating to a virtual environment extends the life of the applications.
Benefits:
- Cost savings: Virtualization often leads to reduced hardware costs and increased resource utilization.
- Easier management: VMs can be more efficiently managed and scaled compared to physical servers.
Considerations:
- Ensure compatibility with the virtualization platform.
- Address differences in hardware configurations between the physical and virtual environments.
2. Virtual to Virtual (V2V) Migration:
Definition:
- V2V migration involves moving a virtual machine (VM) from one virtualization platform to another.
Process:
- The VM is exported or imaged from the source virtualization platform and then imported or deployed on the destination virtualization platform.
Use Cases:
- Platform migration: Organizations might switch virtualization platforms for various reasons, such as cost, features, or vendor preferences.
Benefits:
- Flexibility: Enables organizations to switch between virtualization platforms without the need for physical hardware changes.
- Vendor agnostic: Allows for choosing the virtualization solution that best fits the organization's requirements.
Considerations:
- Compatibility: Verify that the VM format is supported by the destination virtualization platform.
- Address any differences in configurations or features between the two virtualization platforms.
Best Practices for Both Migration Types:
Thorough Planning:
- Conduct a comprehensive assessment of the source environment to identify dependencies and potential issues.
- Develop a detailed migration plan that includes rollback procedures.
Testing:
- Perform thorough testing in a non-production environment to validate the migration process.
- Test the migrated systems to ensure they function as expected in the new environment.
Backup:
- Implement a reliable backup strategy before initiating the migration.
- Have a backup of critical data and configurations to facilitate quick recovery in case of issues.
Communication:
- Communicate the migration plan and potential downtime to relevant stakeholders.
- Provide clear instructions for users and support staff during the migration process.
In conclusion, Alibaba Cloud Migration Service provides a comprehensive solution for organizations seeking to harness the full potential of the cloud. By understanding the diverse benefits, employing effective migration strategies, and following best practices, businesses can seamlessly transition to Alibaba Cloud, unlocking new levels of efficiency, scalability, and innovation. The key lies in careful planning, meticulous execution, and a commitment to leveraging the robust capabilities offered by Alibaba Cloud.